Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Most type of flooring require a substrate to cover imperfections in the subfloor, reduce sound, and provide other benefits specific to each type of floor covering. It may not be exciting, but it is necessary! Choosing the right base product is important to getting a completed project that you’ll really be happy with, but one that many homeowners don’t think about.
Whether you install the underlayment and type of flooring yourself or hire a contractor, this guide will help you achieve the results you want.
Our goal here is to provide a comprehensive underlayment guide that will help you decide the right type for your type of flooring or discuss your options with a flooring contractor.
The Basic Buyers’ Guide includes underlayment prices for each type, top brand names, and an underlay installation overview.
Underlayment is a layer of material located directly under the floor covering. If you are going to tear down the floors in your home, you will likely find many layers. When you remove the floor covering, also called the finishing floor, you will expose the underlayment. Remove that, and you’ll find a subfloor such as OSB (Oriented Strand Board), plywood or concrete. A moisture and/or vapor barrier may exist between layers as well, especially in basement floors, or the substrate may include a barrier in its construction.
Each final type of flooring material requires a specially designed substrate to improve its appearance, performance and durability. Depending on the floor you’re installing, the underlayment may be a solid material such as plywood or cement board, or a soft material such as felt or carpet padding.
Let’s get into detail here with a list of the most common types of underlayment used in type of flooring today. We divide the list by flooring types, so you can zoom in on the right products for your project.
Tile floors remain a popular choice, especially for bathrooms, entryways, and other places where a waterproof surface is required. The impressive variety of tile patterns, shapes, and colors allow you to customize your own design.
The tile underlayment should provide strong support, so that the tile and grout do not crack when you walk on it. However, it should also be somewhat flexible to absorb movement and any expansion or contraction that comes with changing temperature and humidity. Two materials meet these requirements very well.
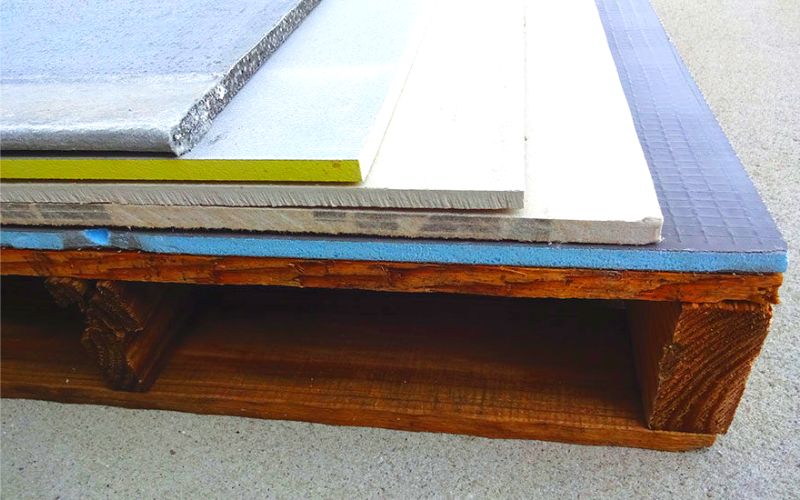

CBU is made of cement and fiber material made from wood or cellulose. The fibers strengthen the cement and also give it a certain amount of flexibility that allows movement without cracking the cement. Cement panels are manufactured in multiple sizes including 3’x5′ which is the most popular and 4’x8′. Typical thicknesses are 1/4″ and 1/2″. It is also called cement backing board.

This premium polyethylene foundation is manufactured with a unique design. DITRA features a grid structure of square grooves, with the base of each grooved larger than the top. This allows the tile mortar, which is attached to the tile, to settle into the cavity when it hardens. Check out our detailed guide to the Schulter Ditra.
The DITRA film, which is 1/8 inch thick, prevents mortar from sticking to the subfloor. Alternatively, the wool backing is laminated with the underside of DITRA, and the backing is glued to the wood or concrete subfloor using a thin mortar.
DITRA is an underlayment that allows movement and expansion/contraction while preventing the transfer of stress that would normally break up grout and tiles. This polyethylene film is an excellent moisture and vapor barrier as well, and can be installed over wood or concrete including floors with radiant heat. Thicker DITRA and DITRA-XL come in 3-inch-wide rolls.

If you have an older home with concrete floors, those lower floors will likely be cracked, uneven, or have low points due to stability. You can’t install type of flooring directly over it and expect the job to look good or last.
The solution to installing floors over concrete that is in poor condition is a self-leveling underlayment, a concrete product that mixes gently and pours easily. Like any liquid, its surface will become flat. This makes a great platform for an additional underlayment such as carpet wadding, DITRA or plywood.
An added benefit of the self-leveling layer is that it works well with radiant floor heating systems. A pipe through which hot water is circulated is laid over the old concrete, and then a self-leveling substrate is poured over the pipe.
Laminate flooring is an attractive, durable alternative to laminate type of flooring, and is usually less expensive. If you purchase quality wood flooring, it may already have a substrate incorporated into its construction. This simplifies installation by eliminating the time-consuming step.
If your product does not have a substrate attached, you will need to select one of these to cover minor defects in the subfloor and give the laminate more stability.
Foam is the basis for wood floors. The foam is 3mm (1/8″) to 6mm (1/4″) thick and comes in rolls of different lengths and widths.
There are two types of foam underlayment – a composite underlayment with an included moisture/vapor barrier and a non-barrier foam. Choose a composite product when installing laminate flooring in a basement or any area, such as a bathroom, where high humidity often produces.
The foam underlayment developed for the sheets is a material that contains rubber or fibers to provide added durability. It also helps reduce the amount of noise passing through the floor from one level to the next.

When you want to reduce the hollow sound of foot traffic, a laminate type of flooring underlayment is the right choice. Cork and felt varieties are available, and most have a moisture barrier included. They are 3 mm (1/8 inch) to 6 mm (1/4″) thick and require only basic skills to install.

For our underlayment discussion, a wide range of hardwood-themed type of flooring comes in. It includes local hardwood floors such as oak, maple, walnut and ash and exotic species such as Brazilian cherry, koa, teak or sakura. Engineered flooring with a layer of solid hardwood on top and layers of composite material underneath. We’ll throw in cork and bamboo as well, since the foundation options are the same as for hardwood.
Felt is most commonly done for hardwood type of flooring , and is usually made in rolls. It is quite dense, and most products are 3 mm (1/8 inch) to 6 mm (1/4″) thick. Felt provides good moisture resistance from below, but in highly humid areas, a moisture barrier should also be installed.
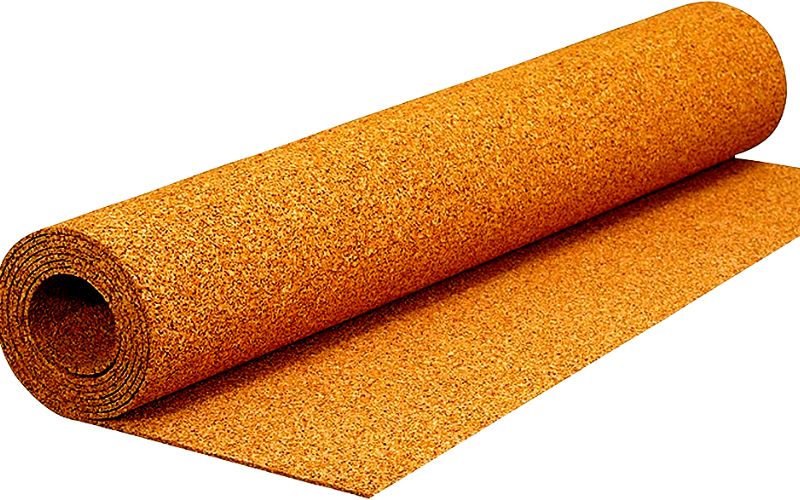


Cork is also used under hardwood floors, and you’ll find products with and without a moisture barrier. In general, wood should be allowed to breathe, thus no moisture barrier is needed.
However, in locations with high humidity, it is safer to use a barrier. Remember, hardwood should not be installed in basements or damp places.
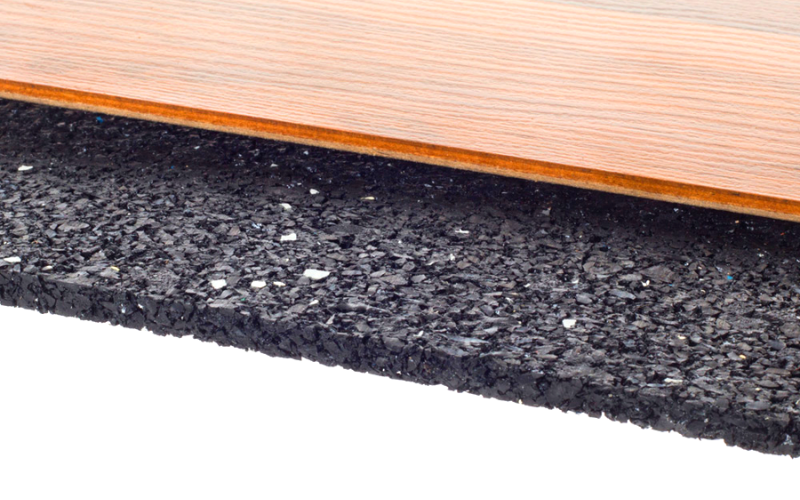

Rubber underlayment is the third choice for use with hardwood floors. In addition to excellent moisture resistance, rubber does a good job of reducing noise. You do not need to glue it, this saves time and effort during installation and removal in the future.
Available from 2mm (5/64″) to 9mm (3/8″), the rubber underlayment provides a moisture barrier and better sound-reducing properties than foam or cork. Rubber also provides superior insulation. It’s easy to work with, but it costs more than other underlayment options.
Foam is a versatile base layer that provides good sound absorption, resists mold and can be recycled. The upgraded foam includes rubber or fibers of another material to increase density, moisture resistance, and durability. You’ve got your choice of foam with an included moisture barrier, often called composite foam, or no-barrier foam. Composite foam is the right choice where there are high humidity conditions in the room or in the space below the room where hardwood floors are installed. This foundation is similar to the foam lining of the plates.
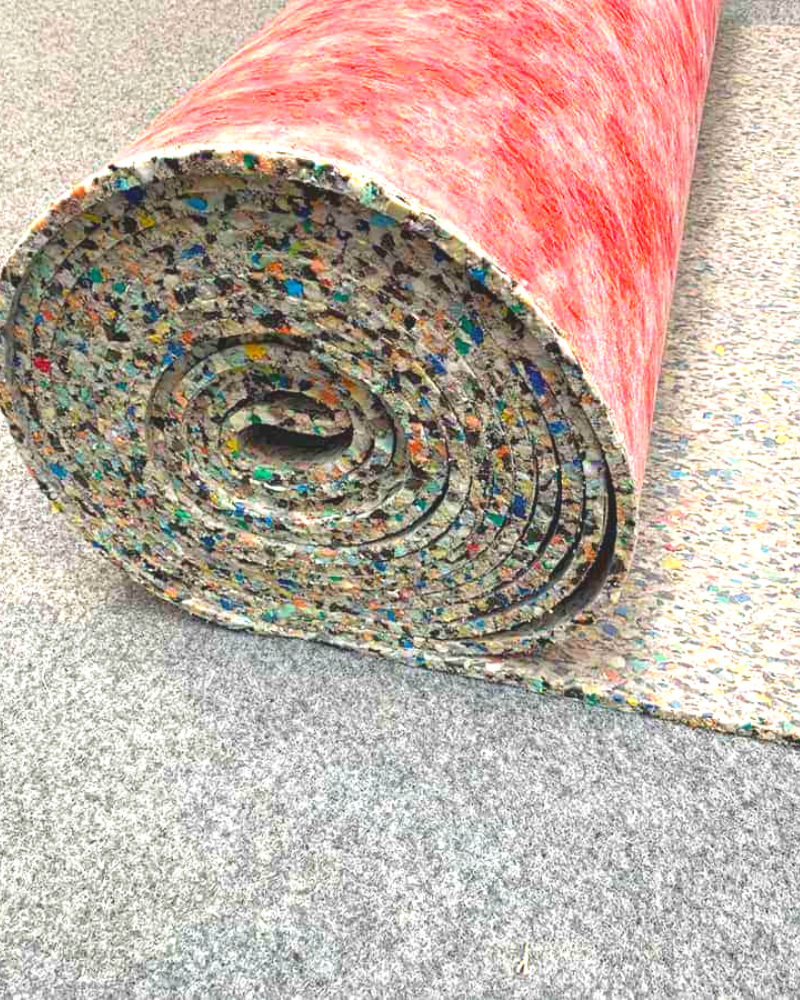

The basic type of carpet is foam or rubber underlayment, especially when the wood or concrete subfloor is in good condition. Backspace options today are greater than ever. Common types include:
Your carpet retailer will be able to suggest the right carpet padding based on the type of subfloor and rug you will be installing. It is perhaps worth noting that Carpet Cushion Council recommends a thickness of at least 1/2″ for cut pile rugs, and less than that for Berber style rugs. Most carpet underpads contain a moisture barrier.

The preferred underlayment for vinyl flooring is 1/4 plywood. Some installers will put vinyl over floors in OSB or plywood if they are in perfect condition. Plywood is available in 4’x8′ and 4’x4′ boards.
If you’re planning a DIY project, take some time to learn everything you can about installation before you begin. In order for your floors to look as good as possible and function as they should, they must be installed correctly. Getting multiple quotes from local flooring contractors is a good idea when hiring a professional to install your flooring. Check their references and learn about their experience. This is the best way to find a quality flooring installer at a competitive price.
Also Read: Concrete Kitchen Flooring